Class 10 Maths
Introduction to Trigonometry

Ex.8.1 Q.1
In Δ ABC, right-angled at B, AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 cm. Determine:
(1) sin A, cos A
(2) sin C, cos C
View Answer
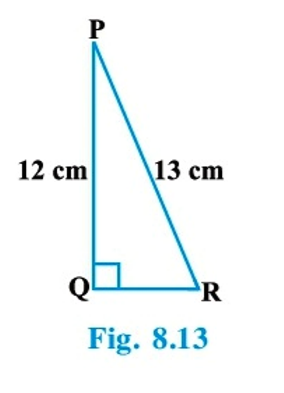
Ex.8.1 Q.2
In Fig. 8.13, find tan P – cot R.
View Answer
Ex.8.1 Q.3
If sin A = , calculate cos A and tan A.
View Answer
Ex.8.1 Q.4
Given 15 cot A = 8, find sin A and sec A.
View Answer
Ex.8.1 Q.5
Given sec θ = , calculate all other trigonometric ratios.
View Answer
Ex.8.1 Q.6
If ∠ A and ∠ B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠ A = ∠ B.
View Answer
Ex.8.1 Q.7
If cot θ = evaluate:
(1) {(1 + sin θ) (1 - sin θ)} ÷ {(1 + cos θ) (1 - cos θ)}
(2) cot2 θ
View Answer
Ex.8.1 Q.8
If 3 cot A = 4, check whether (1 - tan2 A) ÷ (1 + tan2 A) = cos2 A – sin2 A or not.
View Answer
Ex.8.1 Q.9
In triangle ABC, right-angled at B, if tan A = , find the value of:
(1) sin A cos C + cos A sin C
(2) cos A cos C – sin A sin C
View Answer
Ex.8.1 Q.10
In Δ PQR, right-angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm.
Determine the values of sin P, cos P and tan P.
View Answer
Ex.8.1 Q.11
State whether the following are true or false. Justify your answer.
(1) The value of tan A is always less than 1.
(2) sec A = for some value of angle A.
(3) cos A is the abbreviation used for the cosecant of angle A.
(4) cot A is the product of cot and A.
(5) sin θ = for some angle θ.
View Answer
Ex.8.2 Q.1
Evaluate the following:
(1) sin 600 cos 300 + sin 300 cos 600
(2) 2 tan2 450 + cos2 300 – sin2 600
(3) cos 450 ÷ (sec 300 + cosec 300)
(4) (sin 300 + tan 450 – cosec 600) ÷ (sec 300 + cos 600 + cot 450)
(5) (5 cos2 600 + 4 sec2 300 - tan2 450) ÷ (sin2 300 + cos2 300)
View Answer
Ex.8.2 Q.2
Choose the correct option and justify your choice:
(1) 2 tan 300 ÷ (1 + tan2 300) =
(A) sin 600
(B) cos 600
(C) tan 600
(D) sin 300
(2) (1 – tan2 450) ÷ (1 + tan2 450) =
(A) tan 900
(B) 1
(C) sin 450
(D) 0
(3) sin 2A = 2 sin A is true when A =
(A) 00
(B) 300
(C) 450
(D) 600
(4) 2 tan 300 ÷ (1 – tan2 300) =
(A) cos 600
(B) sin 600
(C) tan 600
(D) sin 300
View Answer
Ex.8.2 Q.3
If tan (A + B) = √3 and tan (A – B) = ; 00 < A + B ≤ 900; A > B, find A and B.
View Answer
Ex.8.2 Q.4
State whether the following are true or false. Justify your answer.
(1) sin (A + B) = sin A + sin B.
(2) The value of sin θ increases as θ increases.
(3) The value of cos θ increases as θ increases.
(4) sin θ = cos θ for all values of θ.
(5) cot A is not defined for A = 00.
View Answer
Ex.8.3 Q.1
Express the trigonometric ratios sin A, sec A and tan A in terms of cot A.
View Answer
Ex.8.3 Q.2
Write all the other trigonometric ratios of ∠ A in terms of sec A.
View Answer
Ex.8.3 Q.3
Choose the correct option. Justify your choice.
(1) 9 sec2 A – 9 tan2 A =
(A) 1
(B) 9
(C) 8
(D) 0
(2) (1 + tan θ + sec θ) (1 + cot θ – cosec θ) =
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) -1
(3) (sec A + tan A) (1 – sin A) =
(A) sec A
(B) sin A
(C) cosec A
(D) cos A
(4) (1 + tan2 A) ÷ (1 + cot2 A) =
(A) sec2 A
(B) –1
(C) cot2 A
(D) tan2 A
View Answer
Ex.8.3 Q.4
Prove the following identities, where the angles involved are acute angles for which the expressions are defined.
(1) (cosec θ – cot θ)2 =
(2) +
= 2 sec A
(3) +
= 1 + sec θ + cosec θ
[Hint: Write the expression in terms of sin θ and cos θ]
(4) = sin2 A ÷ (1 – cos A)
[Hint: Simplify LHS and RHS separately]
(5) (cos A – sin A + 1) ÷ (cos A + sin A - 1) = cosec A, using the identity cosec2 A = 1 + cot2 A.
(6) √ {(1 + sin A) ÷ (1 – sin A)} = sec A + tan A
(7) (sin θ – 2 sin3 θ ÷ (2cos3 θ – cos θ) = tan θ
(8) (sin A + cosec A)2 + (cos A + sec A)2 = 7 + tan2 A + cot2 A
(9) (cosec A – sin A) (sec A – cos A) =
[Hint: Simplify LHS and RHS separately]
(10) (1 + tan2 A) ÷ (1 + cot2 A) = (1 - tan2 A) ÷ (1 - cot2 A) = tan2 A
View Answer