Question:
Giving examples, differentiate between roasting and calcination.
Answer:
Roasting is a process of conversion of sulphide ores to oxides by heating the ores in a regular supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. For example, sulphide ores of Zn, Cu, etc. are converted to their oxides in this process.

Calcination is a process of converting hydroxide and carbonate ores to oxides by heating the ores either in the absence or in a limited supply of air and at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. This process leads to the loss of volatile matter leaving behind the metal oxide. For example, hydroxide of Fe, carbonates of Zn, Ca, Mg are converted to their respective oxides by this process.
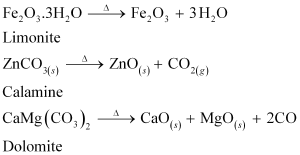
Not what you are looking for? Go ahead and submit the question, we will get back to you.